Rapidly advancing technology has enabled those suffering from hearing loss to take back their independence.
If you’re experiencing hearing problems and are looking for a solution, Bluetooth hearing aids may help you enhance your listening while providing direct streaming to your most commonly used electronics.
This article examines how these Bluetooth-compatible hearing aids work, their advantages and disadvantages, and addresses some of the most commonly asked questions related to the technology.
Key Takeaways
- Bluetooth technology enables wireless communication between electronic devices.
- Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids can remotely connect to any streaming technology that offers Bluetooth connectivity.
- Bluetooth hearing aids allow hands-free streaming from your iPhone, TV, Computer, Android phone, tablet, or another compatible audio device.
- Some hearing aids provide higher audio quality and improved voice localization technology.
- Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids are more expensive and may drain their batteries more frequently than normal ones.
What Are Bluetooth Hearing Aids and How Do They Work?-
Bluetooth hearing aids function as sound amplifiers for individuals with hearing loss while simultaneously allowing them to remotely connect to nearly any Bluetooth-enabled technology within range through a wireless platform.
Most Bluetooth hearing aids can directly link to audio devices like cell phones, TVs, and other Android or IOS technology.
What Is the Advantage of Bluetooth Enabled Hearing Aids?
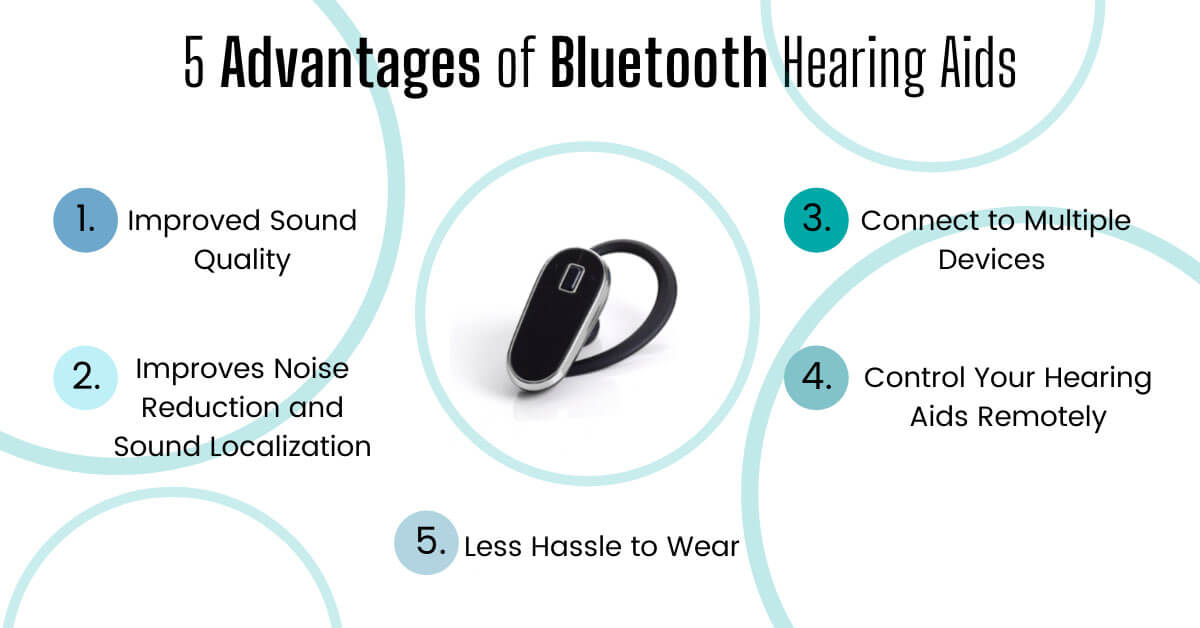
Bluetooth-enabled hearing technology provides a modern alternative to the established sound amplifying technology. Beyond this, they offer distinct advantages over what some may consider outdated standard hearing accessories.
Improved Sound Quality
Connecting directly to your audio devices, Bluetooth hearing aids act similarly to headphones, streaming audio and eliminating the need for actions that may interfere with the quality of the sound they transmit, like putting your cell phone to your ear.
Depending on the type of traditional hearing aid used, this could cause whistling or scratching noise, as well as difficulty finding the correct position for your phone’s speaker [1].
The technology is especially beneficial for people who like listening to music, vastly improving their listening experience. It enables a direct connection to most audio devices while eliminating unnecessary background noise [2].
Improves Noise Reduction and Sound Localization
Individuals making use of hearing aids due to hearing loss often experience a lack of audio localization, making it difficult for them to analyze their surroundings and focus on group conversations [3].
Certain hearing aids can help reduce background noise and improve audio signal localization, better mimicking the hearing abilities of those not suffering from hearing loss.
Control Your Hearing Aids Remotely
Hearing aids that function through Bluetooth connectivity typically come with a simple remote or smartphone installed application that allows you to remotely control your hearing aid volume, switch streaming devices, and connect or disconnect from various audio sources.
Connect to Multiple Devices
Instead of having to remove your hearing aids to listen to music or make calls, only to have to put them back on when you want to watch TV or join a conversation, Bluetooth hearing aids can connect to multiple electronic devices at once and switch seamlessly between them with the click of a button.
Technology capable of connecting to a Bluetooth hearing aid include [4]:
- TVs
- iPads
- iPods, including the iPod Touch
- Any Bluetooth enabled music player (including modern car radios)
- Android smartphones
- Android tablets
- iPhones
- Other Bluetooth audio accessories (using either an IOS or Android platform)
This allows the individual to switch between phone conversations, music streaming platforms, and watching TV in seconds without reconnecting each device.
Less Hassle to Wear
For people who spend a lot of time talking over their mobile phone or participate in sport during which they listen to music, Bluetooth hearing technology can be beneficial as it eliminates the need to remove and replace them repeatedly [5].
Many newer models are far less conspicuous, which could be advantageous for young people who could feel self-conscious while wearing them.
What Are the Disadvantages of Bluetooth Enabled Hearing Aids?
Despite their overall benefits, Bluetooth hearing aids may have several disadvantages related to their connectivity and higher prices.
More Expensive
Good-quality Bluetooth hearing aids can cost anything between $700 and $4000 each, which is substantially pricier than standard devices.
Manufacturers of hearing aid technology are actively attempting to make their Bluetooth-enabled devices more accessible to all budgets. Despite this, they are still more expensive than standard hearing aids.
Drain on Battery Life
Hearing aids reliant on Bluetooth connectivity can quickly drain the battery of the accessories they are connected to, while frequent streaming could do the same to your hearing aid batteries [6].
Ideal standard hearing aid batteries could last up to 132 hours before needing replacement, while Bluetooth ones could run out long before that [7].
The hassle of replacing batteries every four to five days, along with the expenses of doing so, could become a frustrating disadvantage.
Requires Additional Accessories
Some hearing aids may intermittently disconnect from some or be unable to connect to specific audio devices. To prevent this, users may need to purchase a streamer, which links the hearing aid and wireless technology.
Streamers can link multiple electronic devices to your hearing aids through an FM signal.
Having to purchase and carry around extra accessories to ensure your hearing aids work may be a nuisance.
What Are the Best Bluetooth Hearing Aids?
There are many hearing aid brands out there, and deciding which one is right for you could seem overwhelming. Some of the best hearing aids that are Bluetooth enabled are described below.
1. MDHearingAid CORE
As one of the best Bluetooth hearing aids on the market, the MDHearingAid Core is a high-quality device that provides several beneficial features such as:
- A smartphone app allowing you to control and customize your hearing aids with ease
- Noise reduction software
- Directional mics to improve voice localization
MDHearingAid devices are mostly behind-the-ear, which are customizable to fit your ear shape and protect the device from ear wax and moisture in the ear canal.
Other advantages of the MDHearingAid CORE include:
- Affordability: $799.99 for one
- Adjustable hearing profiles to suit your changing hearing abilities
- FDA-registered
Unfortunately, MDHearingAid CORE batteries are not rechargeable, so you must purchase new ones regularly.
2. Oticon More
The Oticon More provides direct streaming from Android, iPhone, and iPad devices. It’s an excellent option for individuals who don’t want to struggle with connecting their devices or purchasing streamers.
Advantages of the Oticon More include:
- Enhanced audio signal streaming, offering not only voice localization but secondary sounds that provide a more satisfactory hearing experience
- Rechargeable batteries that, in most cases, take only three hours to fill
- Water-resistant
- Receiver in canal setup offers a less conspicuous appearance than other hearing aid options
- Control the hearing devices from the Oticon smartphone app
Although the Oticon More is a functional, high-quality device, it is much more expensive than the alternatives, with prices starting at $1,549 for one.
Another disadvantage may be due to slight discomfort from the receiver in canal shape the Oticon More offers. Having something inserted in your ear may feel strange at first and could put some people off of frequently using the devices.
3. ReSound ONE
The ReSound ONE hearing aid is a microphone and receiver-in-ear device which, according to the manufacturers, allows it to collect and amplify sound in a similar way to how your ear naturally would.
The ReSound ONE provides the following advantages:
- Excellent audio signal localization and noise reduction
- Connects to a wide range of devices, including TVs and smartphones, without the need for streamers
- Rechargeable batteries
- Control your settings and monitor your device’s battery on a cell phone app
- Combines three microphones for multi-directional audio detection
The microphone and receiver-in-ear setup may feel a little uncomfortable to some users used to hearing aids fitting along the back of their ears. The devices are also relatively expensive and are not available directly from the hearing aid manufacturer. To purchase one, you must go through a dealer or attempt to do so online.
FAQ
Some of the most frequently asked questions about Bluetooth hearing aids are answered below.
Do Bluetooth Hearing Aids Work?
Yes, Bluetooth hearing aids work. Not only do they help amplify sound to assist individuals experiencing hearing loss, but they allow them to connect their hearing aid to various audio streaming electronic devices at the same time.
Do Bluetooth Hearing Aids Disconnect a Lot?
Your hearing aid may automatically disconnect from your phone or electronic device due to several reasons, including:

- Running out of battery
- Moving out of range
- Being overridden by another device connecting to your phone, iPad, or TV
Unless one of these things has occurred, your Bluetooth hearing aids should not disconnect from any of your devices.
Is It Ok to Use Only One Bluetooth Hearing Aid?
Some people experience hearing loss in only one ear, making it perfectly okay only to use one hearing aid.
However, a regular hearing test should be conducted to ensure the good ear is still hearing normally. If both ears are affected, two hearing aids are advised as they help improve the quality of the sounds heard and provide a more realistic listening experience.
What Is a Bluetooth Hearing Aid Streamer?
A Bluetooth streamer is a small device that turns your hearing aid into a wireless headset. Most hearing aids need a streamer to enable communication and connectivity between them and the target device.
A streamer may also contain a microphone or audio receiver, enabling you to make hands-free phone calls, while a TV streamer is connected directly to your TV and transmits audio straight to your hearing aids [8].
How Much Do Bluetooth Hearing Aids Cost?
A pair of Bluetooth hearing aids can range from $1400 to $8000, depending on the manufacturer and design.
The three most popular hearing aids’ prices are:
- MDHearingAid CORE: $799.99 for one, $999.99 for a pair
- Oticon MORE: $1,549 for one, $2,798 for a pair
- ReSound ONE: $1,675 for one, $2,960 for a pair
How Long Do Bluetooth Hearing Aids Last?
Most hearing aids last between three and seven years, depending on how often you use them, how well they were maintained, and their original quality level.
In-ear hearing aids typically need to be replaced more often than behind-the-ear models.
What Are Universal Bluetooth Hearing Aids?
Universal Bluetooth hearing aids are devices that offer Bluetooth compatibility with any enabled electronic device. These hearing aids connect effortlessly to both Android and IOS devices across various platforms.
However, most Bluetooth hearing aids are either made-for-iPhone or built to work with Android electronics specifically.
To bypass these restrictions, you must use a streamer.
Can You Connect Bluetooth Hearing Aids to TV?
You can connect Bluetooth hearing aids to a TV without interrupting the TV’s stereo sound. Audio input from the TV streams to your hearing aid, although most can only do so through a TV connector, TV adapter, or TV streamer.
Bluetooth hearing aids can also only connect to one TV at a time through the streamer, which means if you have multiple televisions in your home, you’ll have to disconnect and reconnect to whichever device you want to use.
How Do I Connect My Bluetooth Hearing Aid to My Computer?
For universal Bluetooth hearing aids, the process is simple:
- Open your computer’s settings (IOS) or Control Panel (Windows)
- Click on Bluetooth or Connected Devices, or Hardware and Sound
- Search for your hearing aid
- Pair your computer to your hearing aid
If you do not have universal hearing aids, you will need to purchase a streamer through which a connection to your computer may be established according to the streamer’s instructions.
Can I Connect My Bluetooth Hearing Aid to My Phone?
Yes, you can connect your Bluetooth hearing aid to your phone with Bluetooth connectivity.
Through streamers, your Bluetooth hearing aid can connect to any:
- Android mobile phone
- iPhone (using IOS)
Direct audio streaming allows you to make a phone call, listen to music, and listen to video audio completely hands-free.
Do Bluetooth Hearing Aids Have Microphones?
No, not all Bluetooth hearing aids include a microphone. Although some do, many manufacturers have not optimized these microphones for receiving audio from the wearer. If you want to use your mobile phone to make a phone call, you may have to invest in a streamer to act as a mic into which you can talk.
In What Range Do Bluetooth Hearing Aids Work?

Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids typically have a maximum range of 30 feet. In reality, this range is much smaller if there are walls or obstructions between the connected devices.
Are Made-for-iPhone Hearing Aids Compatible With All Bluetooth Devices?
Made-for-iPhone hearing technology can connect directly to your iPhone without the use of a streamer. If you want your hearing aids to connect to an Android device or computer, you will have to purchase a streamer as an intermediary.
Conclusion
Bluetooth-compatible hearing aids can significantly improve your hearing abilities while allowing you to connect to your electronics hassle- and hands-free. If you are searching for an audio enhancement solution to counter your hearing loss, these hearing aids may provide you with the listening assistance and ease of use you need.
References:
- A;, Smith P;Davis. “The Benefits of Using Bluetooth Accessories with Hearing Aids.” International Journal of Audiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25158607/.
- Kim MB;Chung WH;Choi J;Hong SH;Cho YS;Park G;Lee S; “Effect of a Bluetooth-Implemented Hearing Aid on Speech Recognition Performance: Subjective and Objective Measurement.” The Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24687593/.
- Byrne, D, and W Noble. “Optimizing Sound Localization with Hearing AIDS.” Trends in Amplification, SAGE Publications, June 1998, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4172152/.
- CH;, Kim JS;Kim. “A Review of Assistive Listening Device and Digital Wireless Technology for Hearing Instruments.” Korean Journal of Audiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25566400/.
- AM;, Maidment DW;Amlani. “Argumentum Ad Ignorantiam: Smartphone-Connected Listening Devices.” Seminars in Hearing, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33364675/.
- P;, Miegel J;Branch P;Blamey. “Wireless Communication between Personal Electronic Devices and Hearing Aids Using High Frequency Audio and Ultrasound.” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30404497/.
- Helle Strandbygaard Joergensen, Lars Baekgaard. “Battery Consumption in Wireless Hearing Aid Products – Datasheet Helle Strandbygaard Joergensen Lars Baekgaard Benedikte Bendtsen.” AudiologyOnline, 3 June 2013, www.audiologyonline.com/articles/battery-consumption-in-wireless-hearing-11899.
- JA;, Rodemerk KS;Galster. “The Benefit of Remote Microphones Using Four Wireless Protocols.” Journal of the American Academy of Audiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26333880/.






Leave a Reply